NVIDIA GeForce RTX 50 Series: Complete Model Guide
Whether you already own a system powered by an RTX 50 GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) or are considering a purchase that includes one, this guide explains the models, positioning, and practical use cases across the lineup, helping you understand what each GPU is designed to do and who it’s for.
Flagship enthusiast tier
GeForce RTX 5090
The GeForce RTX 5090 sits at the top of the RTX 50 Series and is designed for uncompromised performance. With 32GB of GDDR7 memory and the highest CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) core count in the lineup, it targets 4K and 8K gaming, advanced ray tracing, and demanding creative or AI-assisted workflows.
This GPU is most commonly found in high-end desktops and premium workstations, where power delivery and thermal headroom can support its capabilities.


High-end performance tier
GeForce RTX 5080
The RTX 5080 delivers flagship-class features at a slightly more accessible level. Equipped with 16GB of GDDR7 memory, it is positioned for high-refresh 4K gaming and professional content creation, such as video editing and 3D rendering.
For users who want exceptional performance without stepping up to the RTX 5090, the RTX 5080 offers a strong balance of power and efficiency.
GeForce RTX 5070 Ti
Sitting just below the RTX 5080, the RTX 5070 Ti focuses on high-end 1440p gaming and entry-level 4K experiences. It maintains 16GB of GDDR7 memory, making it well-suited to modern game engines and creative applications that benefit from higher VRAM (Video Random Access Memory) capacity.
Mainstream performance tier
GeForce RTX 5070
The RTX 5070 is positioned as a performance-focused mainstream GPU, ideal for 1440p gaming at high settings with ray tracing and DLSS enabled. With 12GB of GDDR7 memory, it offers a noticeable step up from entry-level models while remaining efficient for compact desktops and laptops.
This model is often included in prebuilt systems aimed at enthusiasts who want strong gaming and creative capabilities without moving into enthusiast-tier pricing.


Entry-level and value-oriented models
GeForce RTX 5060 Ti
Available in 16GB and 8GB variants, the RTX 5060 Ti bridges the gap between mainstream and entry-level GPUs. The higher-memory version is particularly attractive for users working with creative software, large textures, or AI-enhanced applications where VRAM matters.
Both variants support the full RTX feature set, including ray tracing and DLSS 4, making them a solid choice for balanced systems.
GeForce RTX 5060
The RTX 5060 is intended as an accessible entry point into the RTX 50 ecosystem. With 8GB of GDDR7 memory, it targets 1080p gaming and everyday creative workloads while still benefiting from the same architectural advances as higher-end models.
This GPU is commonly found in mid-range desktops and laptops, offering modern graphics features without the power demands of larger cards.
Choosing the right RTX 50 Series GPU
When deciding which RTX 50 Series GPU best suits your needs, consider:
- Target resolution (1080p, 1440p, 4K)
- Workloads beyond gaming, such as content creation or AI-assisted tasks
- System form factor, especially for compact desktops or laptops
- VRAM requirements for future-proofing modern applications
All models share the same core RTX technologies, so even entry-level options benefit from AI-enhanced graphics and real-time ray tracing.
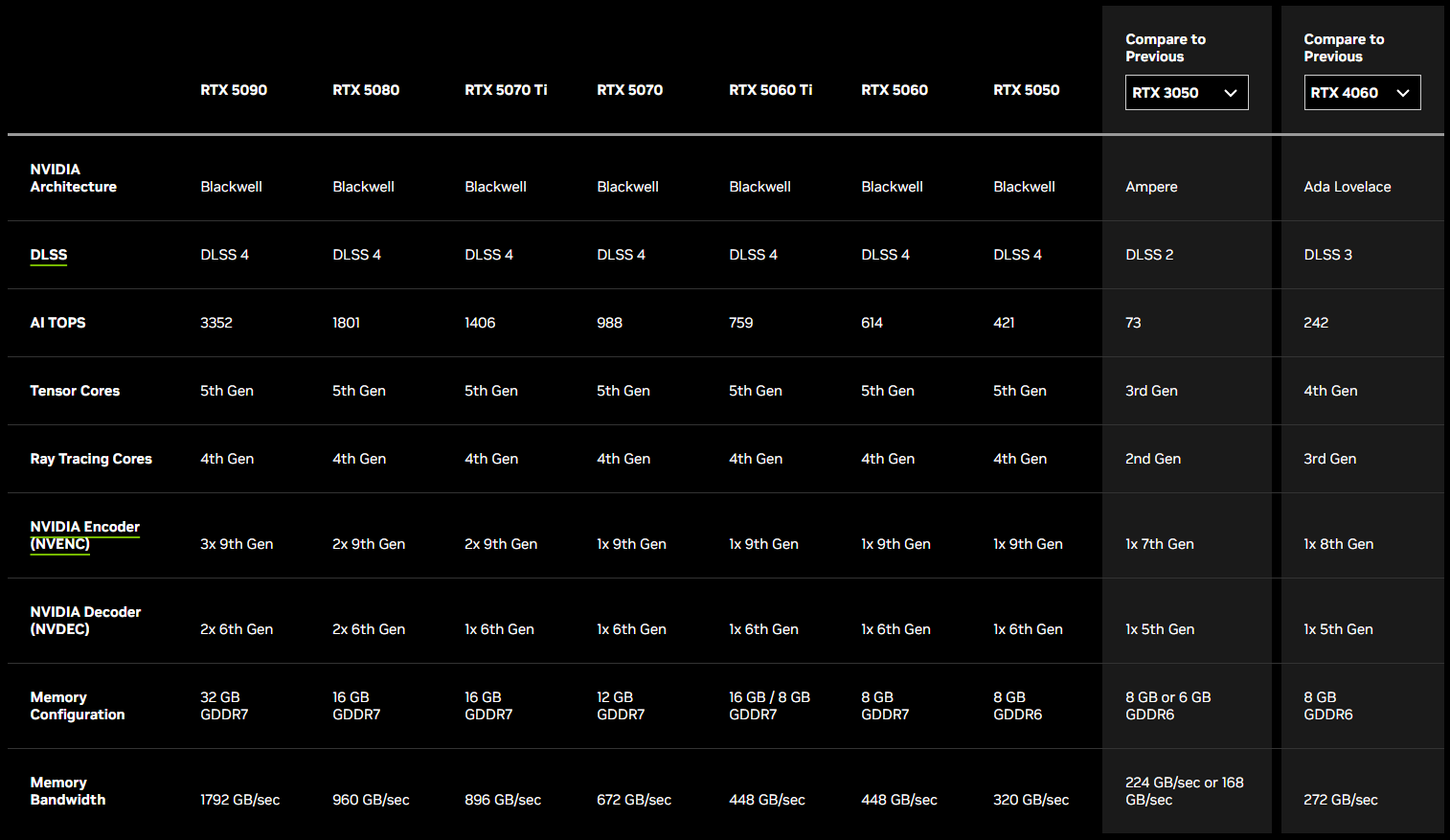
Specifications of the 50 Series
To put the RTX 50 Series into a clearer context, the following comparison table steps back from individual model positioning and looks at headline specifications across generations.
By lining up the full RTX 50 Series against NVIDIA’s previous entry-level baselines—the GeForce RTX 3050 from the 30 Series and the GeForce RTX 4060 from the 40 Series—this snapshot highlights how architectural advances, memory technology, and AI-focused features have evolved over time.
The goal is not to replace in-depth benchmarks, but to give a quick, at-a-glance understanding of generational progress and what those changes mean for customers upgrading or evaluating systems built around modern NVIDIA GPUs.
Whether you already own an RTX 50-powered system or are considering one, understanding the differences between the models helps ensure you choose hardware that matches your performance needs today—and into the future.




